Building and Deploying Application¶
Clone and enter your containers.git:
git clone https://source.foundries.io/factories/<factory>/containers.git
cd containers
Your containers.git repository is initialized with a simple application example in shellhttpd.disabled.
Tip
Directory names ending with .disabled in containers.git are ignored by the FoundriesFactory® CI.
Move the entire application folder shellhttpd.disabled to shellhttpd:
git mv shellhttpd.disabled/ shellhttpd
Commit your changes with a message:
git commit -m "shellhttpd: add application"
Push all committed modifications to the remote repository:
git push
Example Output:
Enumerating objects: 6, done.
Counting objects: 100% (6/6), done.
Delta compression using up to 16 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (5/5), done.
Writing objects: 100% (5/5), 795 bytes | 795.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 5 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
remote: Trigger CI job...
remote: CI job started: https://ci.foundries.io/projects/<factory>/lmp/builds/4/
To https://source.foundries.io/factories/<factory>/containers.git
daaca9c..d7bc382 main -> main
Note
The output of git push indicates the start of a new CI job.
Once your changes to the containers.git repository were pushed, the FoundriesFactory® CI automatically started a new container-main build.
Go to https://app.foundries.io, select your Factory and click on Targets:
The latest Target named containers-main should be the CI job you just created.
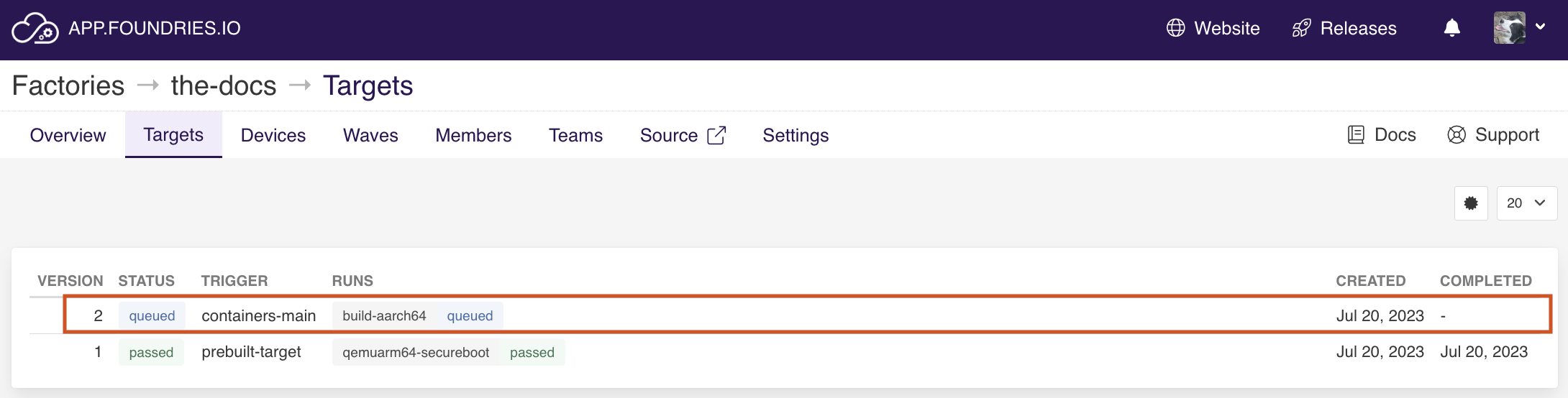
Fig. 9 FoundriesFactory Targets¶
Your device is configured to always download the latest Target version with a specific tag.
By default, devices run all applications defined in the containers.git repo.
This behavior can be changed by enabling only specific applications.
This will be covered this in more detail later.
When the container build finishes, the device will download and start the shellhttpd application.
Check the device status on the devices page and wait the shellhttpd on APPS and the green light on STATUS.
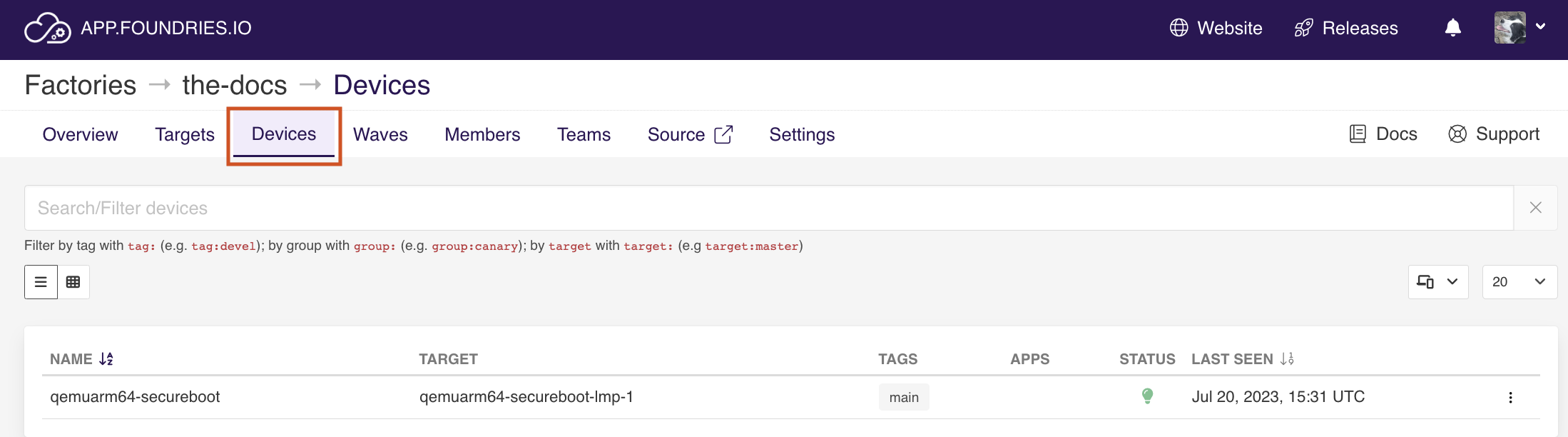
Fig. 10 Device List¶
Testing the Container¶
curl is not available on your device, instead run wget to test the container like so:
wget -qO- 127.0.0.1:8080
Hello world
You can also test the container from an external device connected to the same network, such as your computer.
#Example curl 192.168.15.11:8080
curl <device IP>:8080
Hello world
You can get a more detailed guide by following the next section, Tutorials, starting with Getting Started With Docker.
See also
If you would like to learn about how to customize the platform, checkout both our tutorial, and the user guide on LmP Customization.