Boot Software Updates on iMX
Boot Artifacts
SPL
SPL is the first software loader generated by the i.MX U-Boot build. It is signed via the NXP® CST tool, filling in various IVT header fields. SPL binaries from CI cannot be added directly to OTA due to missing signature data, which must be added by you.
In some cases, an SoC may require additional firmware to be loaded (such as DDR firmware for i.MX 8M). This firmware is loaded prior to the load/verification of U-Boot FIT-image.
U-Boot FIT Image
“U-boot FIT-image” is a generic name for the signed FIT-image containing U-Boot proper (u-boot.bin) and a host of other firmware.
This file is verified by SPL via a public key stored in SPL’s dtb.
This artifact may be signed—on closed boards—as a part of CI, and can be included automatically in a boot software OTA package.
U-boot-nodtb.binU-boot.dtb- OP-TEE
- Arm Trusted Firmware (ARMv8)
- Possibly other firmwares
If the CI signing key has been rotated since the last OTA, then the SPL.dtb verification data needs to be updated prior to booting the new U-Boot FIT-image.
MMC Boot Image Layout
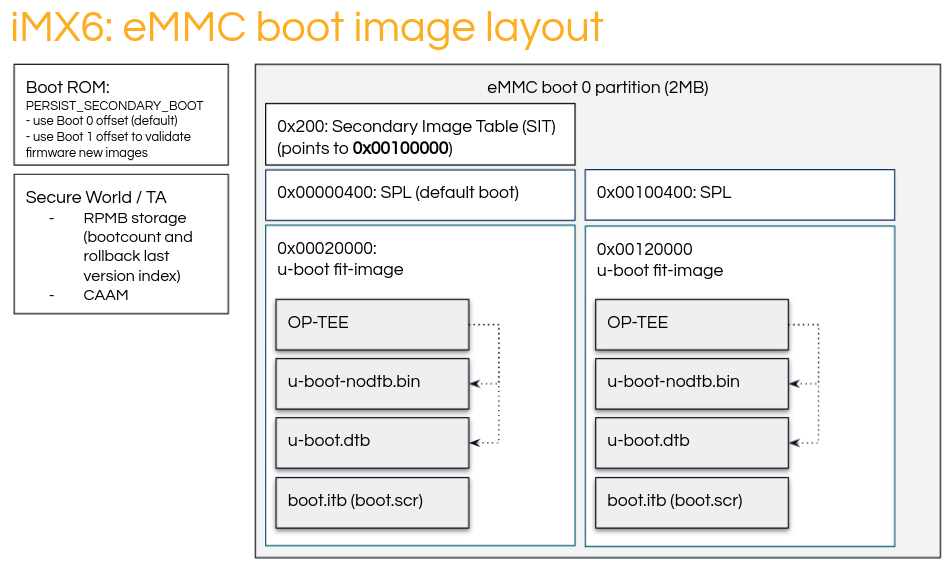
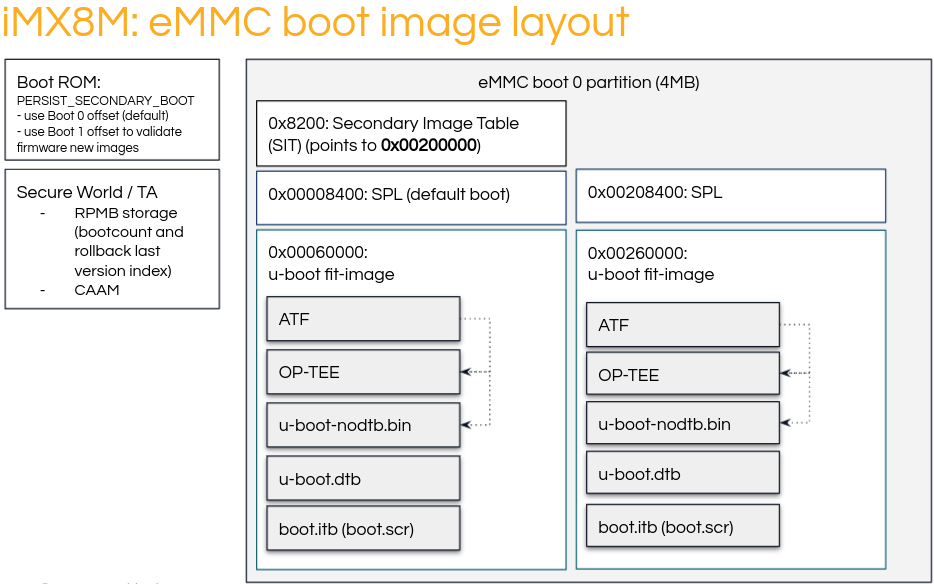
The Secondary Image Table (SIT) is a 20 byte long structure containing 5 32-bit words.
These encode the bootloader B-copy area offset (firstSectorNumber), the magic value (tag) which is always 0x00112233, and three unused words set to 0.
Example SIT:
$ hexdump -vC sit-mx8mm.bin
00000000 00 00 00 00
00000004 00 00 00 00
00000008 33 22 11 00 <--- This is the "tag"
0000000c 00 10 00 00 <--- This is the "firstSectorNumber"
00000010 00 00 00 00
Boot Flow
SPL
- Initialize DDR
- Load U-Boot FIT-image
- Perform verification
- Extract components
- Jump to ATF / OP-TEE
ATF (ARMv8)
- Perform memory permission setup
- Drop to EL-2 non-secure
- Jump to OP-TEE
OP-TEE
- Perform secure world setup
- Driver init
- Load TAs
- Drop to EL-2 secure world
- Jump to
u-boot.bin
U-Boot
- Driver init
- Boot script
- Load kernel FIT-image
- Perform verification
- Extract components
- Jump to Linux kernel
Update Procedure
Primary vs Secondary Boot Paths
There are some i.MX SoCs which can be configured to have two copies of the bootloader in SD/eMMC, and switch between them. The switch can be triggered either by the BootROM—in case the bootloader image is faulty—or can be enforced by the user.
The bootloader A-copy must be placed at a predetermined offset in SD/eMMC. The bootloader B-copy area offset is determined by an offset stored in The Secondary Image Table (SIT). The SIT must be placed at the predetermined offset in SD/eMMC.
To enforce BootROM to boot the secondary boot image, PERSIST\_SECONDARY\_BOOT must be set in the SRC\_GPR10 register, and a warm reset performed.
After reboot, BootROM will boot the image using the offset specified in the SIT table.
For additional details about the SIT format and SIT offsets, please refer to your the SoC Reference Manual, section Redundant boot support for expansion device.
libaktualizr and aktualizr-lite
- Aktualizr-lite decides if boot firmware needs to be updated based on
${ostree\_root}/usr/lib/firmware/version.txt, whereostree\_rootis the root of newly deployed ostree sysroot. Example of contents:bootfirmware\_version=10 - After parsing
bootfirmware\_version, it compares the new version number with the existing one. This is obtained viafiovborubootenv. - If
bootfirmware\_versionfromversion.txtis higher than the existing one, aktualizr-lite setsbootupgrade\_availableviafiovborubootenv. - Reboot should be performed.
U-Boot boot.cmd Script
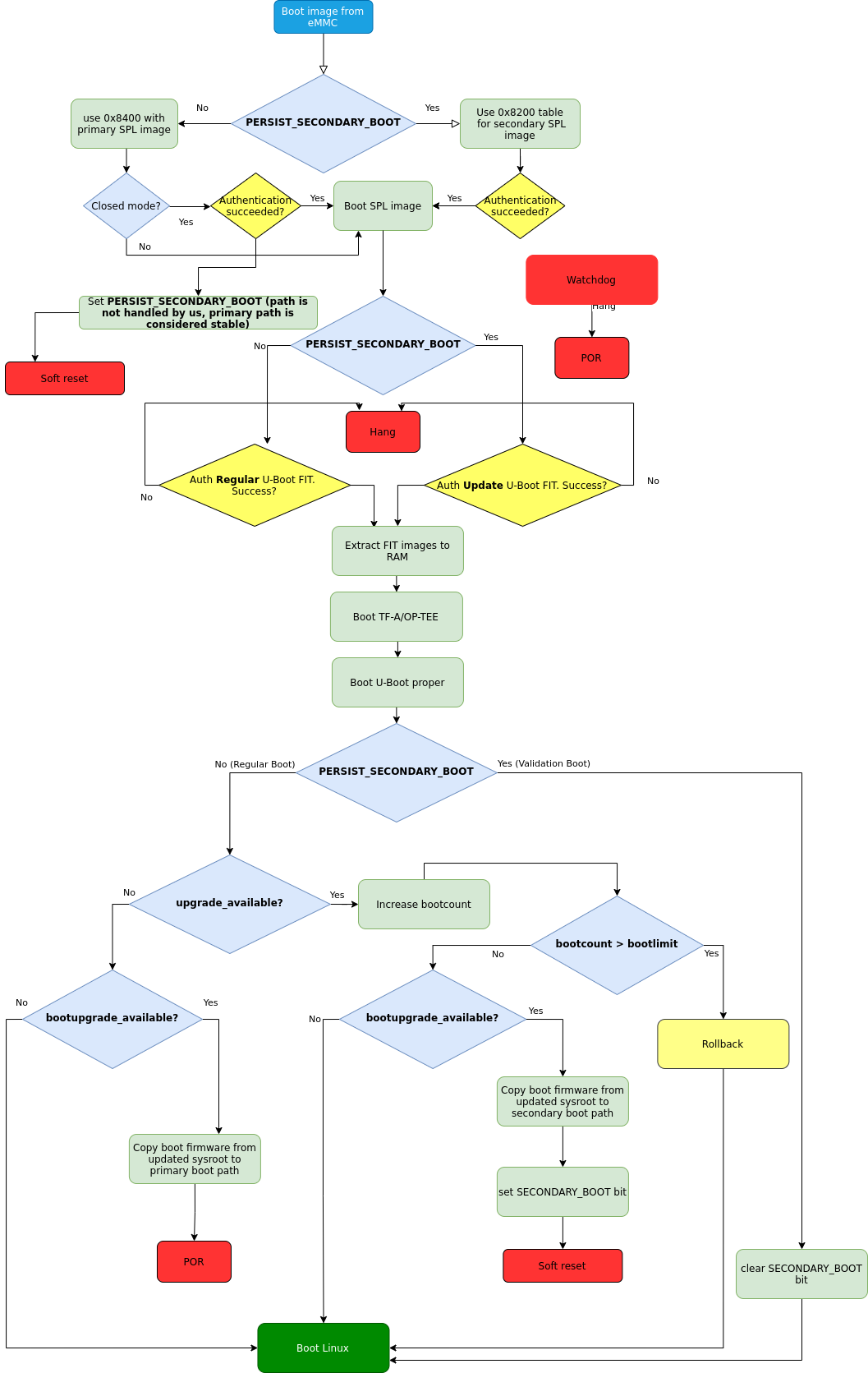
Fig. 88 Boot firmware upgrade flow
- Actual update is done via U-Boot
boot.cmdscript (boot.scr). boot.cmdchecks if the booting secondary path is booted.- In case
upgrade\_availableis set, check if boot firmware upgrade is needed is by checking thebootupgrade\_availableflag. If both are true, obtain boot firmware images from the newly deployed ostree sysroot and write them to secondary boot path offsets. After the secondary boot bit is set, warm reset is performed to enforce BootROM to boot secondary boot path. - After executing rebooting secondary boot path, perform condition verification from step 2. It should evaluate as false, so regular booting of Linux having taken place.
- After Linux is booted, aktualizr-lite confirms a successful update by clearing the upgrade_available flag. At this point, new boot firmware images are validated and need to be flashed to the stable primary path. Additional reboot is needed after this step.
- Regular POR cold reset is performed.
Add a New Board
TF-A/OP-TEE
TF-A on ARMv8, or OP-TEE on ARMv7, provides PSCI services to the Linux® OS and should support the SYSTEM\_RESET2.
This implements a internal warm reset, resetting only the CPU.
This is needed for retaining the values of special registers after reboot.
This behavior differs from a regular SYSTEM\_RESET, which causes POR, removing power for the whole board (resets CPU, DDR and peripherals, on some boards it also resets external PMIC).
U-Boot
SPL: FIT Image Offset Calculation
U-Boot SPL automatically detects which image to boot next based on the SECONDARY_BOOT value.
Every board has the configuration CONFIG\_SYS\_MMCSD\_RAW\_MODE\_U\_BOOT\_SECTOR.
This contains the offset of the U-Boot FIT image, beginning from the boot media sectors (512 bytes each).
Below is an example of how the final offset is calculated on iMX SoCs (extract from ./arch/arm/mach-imx/spl.c):
#if defined(CONFIG_SECONDARY_BOOT_RUNTIME_DETECTION) && \
defined(CONFIG_SYS_MMCSD_RAW_MODE_U_BOOT_USE_SECTOR)
unsigned long spl_mmc_get_uboot_raw_sector(struct mmc *mmc,
unsigned long raw_sect)
{
int boot_secondary = boot_mode_getprisec();
unsigned long offset = CONFIG_SYS_MMCSD_RAW_MODE_U_BOOT_SECTOR;
if (boot_secondary) {
offset += CONFIG_SECONDARY_BOOT_SECTOR_OFFSET;
printf("SPL: Booting secondary boot path: using 0x%lx offset "
"for next boot image\n", offset);
} else {
printf("SPL: Booting primary boot path: using 0x%lx offset "
"for next boot image\n", offset);
}
return offset;
}
#endif
Fastboot: Support of Secondary Boot Image Offsets
The required offsets for the secondary boot images (SPL, U-Boot.itb, and SIT) for iMX6, iMX6ULL, iMX7, and iMX8M SoCs are defined by the FSL fastboot driver.
To change the SIT offset used for an SoC,
adjust the secondary\_image\_table\_mmc\_offset() and bootloader\_mmc\_offset() functions within the U-Boot fastboot driver source (drivers/fastboot/fb\_fsl/fb\_fsl\_partitions.c).
Secondary Image Table Generation
SIT image binary is generated automatically if U-Boot is being built with the correct value for the CONFIG\_SECONDARY\_BOOT\_SECTOR\_OFFSET config option.
Watchdog
The secondary boot path is mainly used for boot firmware update image validation.
In exceptional cases it will behave incorrectly, such as the system not responding.
To address such cases, watchdog support has to be enabled in SPL.
This is done by adding the following config options to lmp.cfg:
CONFIG_IMX_WATCHDOG=y
CONFIG_SPL_HW_WATCHDOG=y
# CONFIG_SPL_WDT is not set
CONFIG_SPL_WATCHDOG_SUPPORT=y
meta-lmp
MfgTool Scripts
To deploy boot images to the destination board, the mfgtools package is used.
It uses a special configuration file with uuu extensions, which contains all instructions needed for the deployment of boot images.
Default uuu files do not support flashing images for secondary boot path.
Doing so requires the following adjustments: adding SIT image, secondary SPL, and U-Boot FIT deployment steps:
+FB: flash bootloader_s ../imx-boot-@@MACHINE@@
+FB: flash bootloader2_s ../u-boot-@@MACHINE@@.itb
+FB: flash sit ../sit-@@MACHINE@@.bin
The final uuu script looks like:
uuu_version 1.2.39
SDP: boot -f imx-boot-mfgtool
SDPS: boot -f imx-boot-mfgtool
SDPV: delay 1000
SDPV: write -f u-boot-mfgtool.itb
SDPV: jump
FB: ucmd setenv fastboot_dev mmc
FB: ucmd setenv mmcdev ${emmc_dev}
FB: ucmd mmc dev ${mmcdev} 1; mmc erase 0 0x2000
FB: flash bootloader ../imx-boot-@@MACHINE@@
FB: flash bootloader2 ../u-boot-@@MACHINE@@.itb
FB: flash bootloader_s ../imx-boot-@@MACHINE@@
FB: flash bootloader2_s ../u-boot-@@MACHINE@@.itb
FB: flash sit ../sit-@@MACHINE@@.bin
FB: ucmd if env exists emmc_ack; then ; else setenv emmc_ack 0; fi;
FB: ucmd mmc partconf ${mmcdev} ${emmc_ack} 1 0
FB: done
lmp.cfg Files
To enable support for flashing/booting secondary boot images, adjust both the default lmp.cfg, and the one for mfgtools.
The following config options need to be added to the default lmp.cfg:
CONFIG_SECONDARY_BOOT_RUNTIME_DETECTION=y
CONFIG_SECONDARY_BOOT_SECTOR_OFFSET=0x1000
CONFIG_CMD_SECONDARY_BOOT=y
And to mfgtool lmp.cfg:
CONFIG_FSL_FASTBOOT_BOOTLOADER_SECONDARY=y
CONFIG_SECONDARY_BOOT_SECTOR_OFFSET=0x1000
Pre-Load boot.cmd by SPL
As boot.cmd depends on U-Boot commands for booting Linux, it should be aligned with the U-Boot version.
By default, in setups without boot firmware update support, boot.cmd is stored in the first FAT partition in eMMC/SD.
To get boot.cmd updates—together with other boot software images—it should be moved from the FAT partition, to the U-Boot FIT image.
To do this, edit lmp-machine-custom.inc, adding this line for your board (imx8mqevk used as an example):
BOOTSCR_LOAD_ADDR_imx8mqevk = "0x44800000"
This change will include Linux boot.cmd into the U-Boot FIT image, alongside TF-A/OP-TEE/U-Boot proper/U-Boot dtb images.
When SPL parses the U-Boot FIT image (u-boot.itb) it will pre-load boot.itb (compiled and wrapped boot.cmd) to the address specified in BOOTSCR\_LOAD\_ADDR variable.
To let U-Boot know where to get the boot script from, you should also adjust CONFIG\_BOOTCOMMAND in the U-Boot lmp.cfg of your board.
CONFIG_BOOTCOMMAND="setenv verify 1; source 0x44800000; reset"
Test Basic API
After applying all the updates from previous steps, we should validate that everything is in place. This consists of two steps:
- Cold/Warm resets from U-Boot are functional
- Obtain board security state (open/closed states)
To test cold/warm resets and booting primary/secondary boot path, use these two U-Boot commands imx\_secondary\_boot and resetreset -w (warm reset).
Tip
For regular reset, usually it does
POR.
Example of test:
U-Boot SPL 2020.04+fio+gee4483499f (Jan 01 1970 - 00:00:00 +0000)
Trying to boot from MMC1
SPL: Booting primary boot path: using 0x300 offset for next boot image
...
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0
u-boot => imx_secondary_boot 1
u-boot => reset -w
Resetting...
U-Boot SPL 2020.04+fio+gee4483499f (Jan 01 1970 - 00:00:00 +0000)
Trying to boot from MMC1
SPL: Booting secondary boot path: using 0x1300 offset for next boot image
...
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0
From the output, you can see that after setting secondary boot and performing warm reset,
BootROM boots images from secondary boot path (SPL: Booting secondary boot path: using 0x1300 offset for next boot image).
To check if the security status of your board is detected correctly, use the imx\_is\_closed command:
u-boot=> imx_is_closed
Board is in open state
boot.cmd
Currently, LmP uses template-based generation for the final boot.cmd.
It is constructed from common boot files (./meta-lmp-base/recipes-bsp/u-boot/u-boot-ostree-scr-fit),
which contains all SoC agnostic DEFINE statements and common functionality, and board specific boot.cmd, which includes the common scripts.
Example of board boot.cmd
(./meta-lmp-bsp/recipes-bsp/u-boot/u-boot-ostree-scr-fit/imx8mm-lpddr4-evk/boot.cmd):
echo "Using freescale_${fdt_file}"
# Default boot type and device
setenv bootlimit 3
setenv devtype mmc
setenv devnum 2
setenv bootpart 1
setenv rootpart 2
# Boot image files
setenv fdt_file_final freescale_${fdt_file}
setenv fit_addr ${initrd_addr}
# Boot firmware updates
# Offsets are in blocks (512KB each)
setenv bootloader 0x42
setenv bootloader2 0x300
setenv bootloader_s 0x1042
setenv bootloader2_s 0x1300
setenv bootloader_image "imx-boot"
setenv bootloader_s_image ${bootloader_image}
setenv bootloader2_image "u-boot.itb"
setenv bootloader2_s_image ${bootloader2_image}
setenv uboot_hwpart 1
@@INCLUDE_COMMON_IMX@@
@@INCLUDE_COMMON@@
Above you can find that the only needed variables that should be defined are: boot/root partition indexes, mmc device index, and fdt\_file.
For boot firmware update functionality, bootloader image offsets and names should also be provided.
Sysroot and Signed Boot Artifacts
All boot artifacts (SPL/imx-boot and U-Boot FIT) are automatically deployed to sysroot during build time. However, on closed boards where the initial boot image has to be signed in advance by a subscriber private key, there is way to add a signed binary instead of automatic inclusion of unsigned boot artifacts.
To do this, add lmp-boot-firmware.bbappend to your meta-subscriber-overrides layer, adding the path to the signed binary and the signed binary itself.
Next, define the boot firmware version by setting the LMP_BOOT_FIRMWARE_VERSION global variable in your lmp-factory-custom.inc.
Boot firmware version information will be automatically added to ${osroot}/usr/lib/firmware/version.txt and the U-Boot Device Tree Blob.
Note
The signed binary is called SPL for i.MX 6/7, and imx-boot for i.MX 8* platforms.
No need to append .signed to the binary name.
Example:
diff --git a/recipes-bsp/lmp-boot-firmware/lmp-boot-firmware.bbappend b/recipes-bsp/lmp-boot-firmware/lmp-boot-firmware.bbappend
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6c11380
--- /dev/null
+++ b/recipes-bsp/lmp-boot-firmware/lmp-boot-firmware.bbappend
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+FILESEXTRAPATHS:prepend := "${THISDIR}/${PN}:"
+
+SRC_URI = " \
+ file://SPL \
+"
diff --git a/conf/machine/include/lmp-factory-custom.inc b/conf/machine/include/lmp-factory-custom.inc
index 0fe26b8..2a9815d 100644
--- a/conf/machine/include/lmp-factory-custom.inc
+++ b/conf/machine/include/lmp-factory-custom.inc
@@ -22,4 +22,4 @@ UEFI_SIGN_KEYDIR = "${TOPDIR}/conf/factory-keys/uefi"
# TF-A Trusted Boot
TF_A_SIGN_KEY_PATH = "${TOPDIR}/conf/factory-keys/tf-a/privkey_ec_prime256v1.pem"
+LMP_BOOT_FIRMWARE_VERSION:imx8mm-lpddr4-evk = "3"
diff --git a/recipes-bsp/lmp-boot-firmware/lmp-boot-firmware/SPL b/recipes-bsp/lmp-boot-firmware/lmp-boot-firmware/SPL
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..50f5013
Binary files /dev/null and b/recipes-bsp/lmp-boot-firmware/lmp-boot-firmware/SPL differ
Note
As LMP_BOOT_FIRMWARE_VERSION is now the preferred way to set boot firmware version, defining PV in lmp-boot-firmware.bbappend is deprecated and should not be used.
To switch to the new approach, remove PV = "<version>" from lmp-boot-firmware.bbappend, and define LMP_BOOT_FIRMWARE_VERSION with the appropriate version value as shown above in the example.