Beaglebone Black¶
Preparation¶
Ensure you replace the <factory> placeholder below with the name of your
Factory.
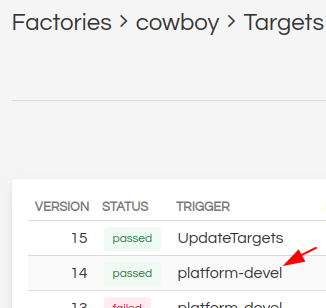
Download necessary files from
https://app.foundries.io/factories/<factory/targets
Flashing¶
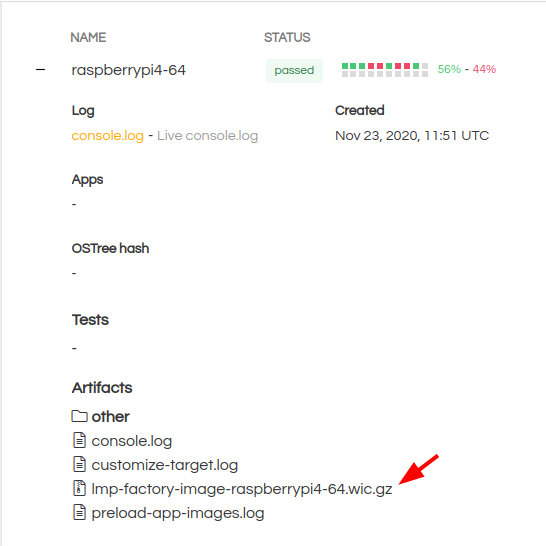
Now, flash the lmp-factory-image-beaglebone-yocto.wic.gz retrieved from the
previous section to an SD Card. This contains the system image that the
device will boot.
By default Beaglebone Black boots from internal eMMC. There are several ways to avoid this:
Press S2 button before powering on
This causes boot sequence to start from SPI0 followed by SD card. If the board is not connected to any SPI boot source SD card should be used
Erase eMMC or disable ‘bootable’ flag on eMMC boot partition
Determine the disk you want to flash by finding the device with the
SIZEthat matches your SD card in the list below. Be sure to ignore partitions (whereTYPEispart). Save theNAMEfor your SD card device to be used in a later step as the disk path. e.g:/dev/mmcblk0:lsblk -po +MODEL
Example Output:
$ lsblk -po +MODEL NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT MODEL /dev/mmcblk0 179:0 0 29.8G 0 disk ├─/dev/mmcblk0p1 179:1 0 41.6M 0 part /mnt/boot └─/dev/mmcblk0p2 179:2 0 29.8G 0 part /mnt/otaroot /dev/zram0 254:0 0 26G 0 disk /out /dev/nvme0n1 259:0 0 953.9G 0 disk SSDPEKKF010T8 NVMe INTEL 1024GB
Flash the disk.
Replace<system-image>with the path to your system image.Replace/dev/mmcblk<X>with your chosen disk path.
gunzip -c <system-image> | sudo dd of=/dev/mmcblk<X> bs=4M iflag=fullblock oflag=direct status=progress
Determine the disk you want to flash by finding the device with the
SIZEthat matches your SD card in the list below. Be sure to ignore partitions (lines without the * in theSIZE). Save theIDENTIFIERfor your SD card device to be used in a later step as the disk path. e.g:/dev/disk3:diskutil list
Example Output:
$ diskutil list /dev/disk3 (internal, physical): #: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER 0: FDisk_partition_scheme *15.5 GB disk3 1: Windows_FAT_32 boot 45.7 MB disk3s1 2: Linux 15.5 GB disk3s2
Flash the disk.
Replace<system-image>with the path to your system image.Replace/dev/disk<X>with your chosen disk path.
gunzip -c <system-image> | sudo dd of=/dev/disk<X> bs=4M
Windows has no dd like tool built into the operating system to flash
your image to disk. In this case, we recommend you download and use either
Win32 Disk Imager or Rufus.
Note
Your system image is in a compressed wic.gz format. To follow these next steps, you must extract it using a tool like 7zip which will leave you with a .wic image file.
Using Rufus
- Download and run Rufus.
- Select your disk.
- SELECT your
<system-image>. - START the flash procedure.
Using Win32 Disk Imager
- Download and run Win32 Disk Imager as Administrator.
- Click the blue folder icon.
- Select your
<system-image> - Select your disk via the Device dropdown.
- Click Write
- Wait for the image to finish writing, and a Write Successful dialog will appear.