Flash your Device¶
Note
- To follow this section, you will need:
- A supported board.
- Capable of booting from eMMC (recommended if available)
- Or capable of booting from a suitable microSD Card
- Wired or WiFi network with internet access.
- Ethernet cable (if choosing Wired)
- Console access to your hardware via display/keyboard or serial (if choosing WiFi)
- A supported board.
Download LmP system image¶
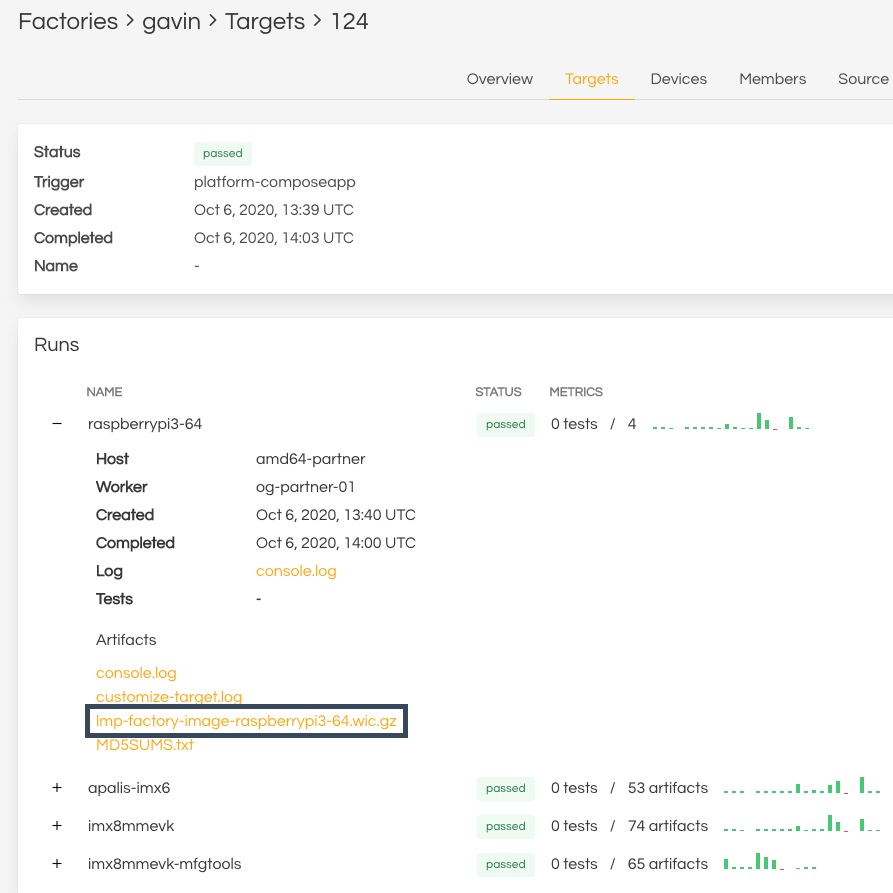
When you trigger a build, it produces build artifacts as an output which can be downloaded from the Targets tab of your factory, as described in Watch Your Build.
Navigate to the Targets section of your Factory.
Find your LmP platform build, denoted by the Trigger name:
platform-<tag>.e.g:
lmp-factory-image-machine-name.wic.gzDownload it by clicking on its name in the list of artifacts.
Flash LmP system image¶
Note
If you are developing on a platform that has eMMC available such as the NXP iMX8MM-EVK, it is recommended that you boot from eMMC rather than SD. Read the Supported Machines section for specific details on flashing your system-image using the vendor provided tools.
Determine the disk you want to flash by finding the device with the
SIZEthat matches your SD card in the list below. Be sure to ignore partitions (whereTYPEispart). Save theNAMEfor your SD card device to be used in a later step as the disk path. e.g:/dev/mmcblk0:Example Output:
Flash the disk.
Replace<system-image>Replace/dev/mmcblk<X>with your chosen disk path.
Determine the disk you want to flash by finding the device with the
SIZEthat matches your SD card in the list below. Be sure to ignore partitions (lines without the * in theSIZE). Save theIDENTIFIERfor your SD card device to be used in a later step as the disk path. e.g:/dev/disk3:Example Output:
Flash the disk.
Replace<system-image>Replace/dev/disk<X>with your chosen disk path.
Windows has no dd like tool built into the operating system to flash
your image to disk. In this case, we recommend you download and use either
Win32 Disk Imager or Rufus.
Note
Your system image is in a compressed wic.gz format. To follow these next steps, you must extract it using a tool like 7zip which will leave you with a .wic image file.
Using Rufus
- Download and run Rufus.
- Select your disk.
- SELECT your
<system-image>. - START the flash procedure.
Using Win32 Disk Imager
- Download and run Win32 Disk Imager as Administrator.
- Click the blue folder icon.
- Select your
<system-image> - Select your disk via the Device dropdown.
- Click Write
- Wait for the image to finish writing, and a Write Successful dialog will appear.
Boot Device and Connect to the Network¶
- Ethernet (Recommended)
- WiFi
Ethernet works out of the box if a DHCP server is available on the local network.
- Connect an Ethernet cable to the board.
- Remove the SD card from your computer, and insert it into the board.
- Apply power to the board.
Your board will connect to the network via Ethernet and will be ready to connect within a minute or two of booting.
Log in via SSH¶
Use fio as the username and machine-name.local as the
hostname:
The default password is fio; we recommend changing it once logged in.
Note
Your device hostname will be defaulted to the value of the machine: key
value from your factory-config.yml Read the Supported Machines
section for a list of supported hardware and their MACHINE value.
Here are some examples:
raspberrypi3-64.localimx8mmevk.localbeaglebone-yocto.localintel-corei7-64.localFor this to work, your PC needs to support zeroconf the hostname must be otherwise unclaimed. If this doesn’t work, you can also log in by IP address. See Troubleshooting below for advice.
Troubleshooting¶
If the above methods to connect your device to the network don’t work, try one of the following.
Temporarily enable and connect to the UART (see directions above in the WiFi section) and determine available IP addresses with:
Then connect by IP address:
List connected devices and their local IP addresses on your network router’s administrative interface, and log in by IP address as above.